The dilemma of production planning - between delivery capability, inventories and capacity utilization
A universal problem in production planning
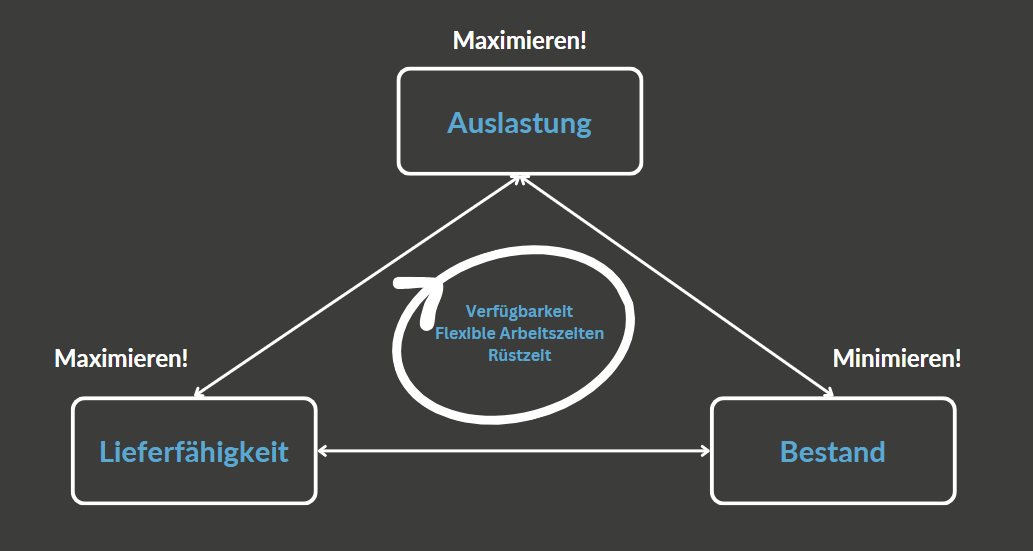
In one of our recent interviews with a practice partner from the manufacturing industry, it quickly became clear that production planning is not a simple optimization problem, but rather a permanent balance between competing target values. Our interviewee spoke of a “triangle” that illustrates the central challenges of production planning: Delivery capability, inventories and capacity utilization. Every company faces the challenge of reconciling these three factors – a task that resembles a dilemma.
In our last blog article, we showed why production planning is more complex than you might think. This article goes one step further and sheds light on how companies can deal with the typical conflicts of objectives between delivery capability, inventories and capacity utilization.
The three central points of conflict
1. delivery capability: The top priority of many companies is to deliver to customers on time. A high delivery rate is crucial for customer satisfaction and long-term business relationships. However, a high delivery capability often means that safety stocks have to be maintained or that production processes are made excessively flexible – both of which can result in high costs.
2. inventories: In order to be able to deliver at all times, companies could keep large quantities of raw materials, semi-finished and finished goods in stock. However, high inventories mean tying up capital, high storage costs and the risk of obsolete products. Especially in a volatile market environment, holding too much stock is a strategic mistake.
3. capacity utilization: The optimal use of machines and personnel is an essential goal in production planning. High capacity utilization increases efficiency, reduces unit costs and maximizes yield. However, full capacity utilization can lead to long throughput times and significantly limit the company’s ability to react to short-term changes.
Process planning vs. scheduling - a distinction from science
In the scientific literature, the dilemma of production planning is often divided into two main areas: Sequencing and scheduling. These two sub-aspects highlight different but closely linked conflicting objectives (Erlach, 2020).
The scheduling dilemma
The aim of process planning (also known as scheduling) is to fulfill customer orders on time while ensuring consistent utilization of production capacity. But this is precisely where the dilemma arises:
- High adherence to deadlines requires flexible production with small batch sizes, but this often leads to increased set-up times and inefficient machine utilization.
- Conversely, high machine utilization with large batch sizes ensures low unit costs, but comes at the expense of flexibility and increases throughput times.
- Fluctuating customer demand also makes planning more difficult, as consistent production capacity utilization often collides with unpredictable fluctuations in demand
The replenishment dilemma
The aim of materials planning is to ensure a high level of delivery capability without building up unnecessarily high stock levels. However, this leads to contradictory requirements:
- High material availability reduces the risk of production delays, but requires extensive inventories with high capital commitment costs.
- Lean warehousing reduces costs, but increases the risk of supply bottlenecks and impairs adherence to delivery dates.
- Although short replenishment times are desirable, they are often associated with smaller, more frequent orders, which in turn result in higher ordering and transportation costs.
Practical experience: making the production dilemma manageable
Production planning remains a central challenge, as it represents a permanent field of tension between competing goals such as delivery capacity, inventories and machine utilization. Companies must constantly make decisions that are always associated with conflicting objectives. There is no complete solution to this dilemma – but there are ways to better manage it.
Many companies today rely on traditional ERP or PPS systems to optimize their production planning. However, these systems quickly reach their limits as they mostly use static rules and simple algorithms. Although they offer transparency regarding resources and capacities, they cannot react flexibly to unforeseen changes. However, the reality of production planning is dynamic: fluctuations in demand, unexpected bottlenecks or machine downtimes make adaptive and intelligent control necessary.
A promising approach to better manage the production dilemma is to simulate different scenarios and test their impact on key performance indicators. This enables companies to make informed decisions, set priorities and identify potential risks at an early stage. Transparent communication also plays a key role here: decision-makers and teams need to understand why certain measures are being taken and how they affect the overall goal.
Modern methods for mastering the production dilemma
Innovative approaches are required to make the production planning dilemma controllable. This is where three key technologies come into play:
- Dynamic adaptation: instead of relying on rigid planning, intelligent systems enable continuous simulation of alternative production scenarios. This allows optimal adjustments to be made in real time.
- Multi-criteria optimization: Instead of just maximizing a single target variable such as machine utilization or stock levels, modern systems take all relevant influencing factors into account simultaneously and look for the best compromise.
- Predictive analytics: By using AI and machine learning, companies can evaluate data, recognize patterns and take preventative measures. This allows potential bottlenecks or machine downtimes to be predicted at an early stage.
AI-supported planning as a solution for the future
Artificial intelligence takes production planning to a new level by supporting data-driven decisions and helping companies to better deal with uncertainties. While traditional ERP systems only map past data, AI-supported planning can make proactive recommendations. It analyzes in real time which adjustments enable the best balance between delivery capability, inventories and capacity utilization and proposes specific measures.
Companies that rely on AI-based solutions at an early stage can not only increase their efficiency, but also react more flexibly and resiliently to market changes. In a constantly changing production landscape, the use of intelligent technologies is increasingly becoming a competitive advantage – and a necessity.
Conclusion: A balancing act with optimization potential
Production planning remains a challenge that cannot be solved by simple rules. Companies that manage to optimally balance their own “production triangle” will secure competitive advantages in the long term. AI-based systems offer new opportunities to create transparency and support decision-makers with well-founded recommendations in real time.
The future of production planning lies in intelligent networking – those who master the dilemma will not only produce more efficiently, but will also be able to react more quickly and flexibly to market changes.
Would you like to find out how your company can benefit from modern planning solutions? Arrange a personal consultation with an expert now and receiqe tailored recommendations for your planning: Book an appointment
Source: Erlach, K. (2020). Wertstromdesign: Der Weg zur schlanken Fabrik. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-58907-6